Spotify Integration with Next.js
Dhruv Gursahani / Nov 13, 2022
8 min read • ––– views

Table of contents 📃
- Intro
- Registering Your App
- Authenticating Your Account
- Saving Sensitive Data to ENV file
- Requesting Access Token
- Top Tracks Data from Spotify
- Now Playing Data from Spotify
- Wrap Up
Intro
In this article, we'll cover how to create a brand new Spotify developer account, mint a refresh token, send request to Spotify's API from your Next app and then deploy it to production using Vercel. As an added bonus this guide will use Typescript and Vercel's Edge functions
Registering Your App
Before we can request data from the Spotify Web API, we need to set up a Spotify developer account. This will allow our website to communicate with the Spotify Web API.
Go to your Spotify Developer Dashboard and log in.
- Click Create an App.
- Enter Application Name and Application Description and then click CREATE.
- Click Show Client Secret.
- Save your Client ID and Client Secret.
- Click Edit Settings. Add your website URL. // Ex.: https://localhost:3000 (This can be changed after deployment).
- Add http://localhost:3000/callback as redirect URI. // Spotify will whitelist this endpoint and sends the code for authorization
All done! You now have a properly configured Spotify application and the correct credentials to make requests.
NOTE:
Client ID is the unique identifier of your application. Client Secret is the key that you pass in secure calls to the Spotify Accounts and Web API services. Always store the client secret key in an
envfile. If you suspect that the secret key has been compromised, regenerate it immediately by clicking "SHOW CLIENT SECRET" then the "RESET" button from your app's dashboard.
Authenticating Your Account
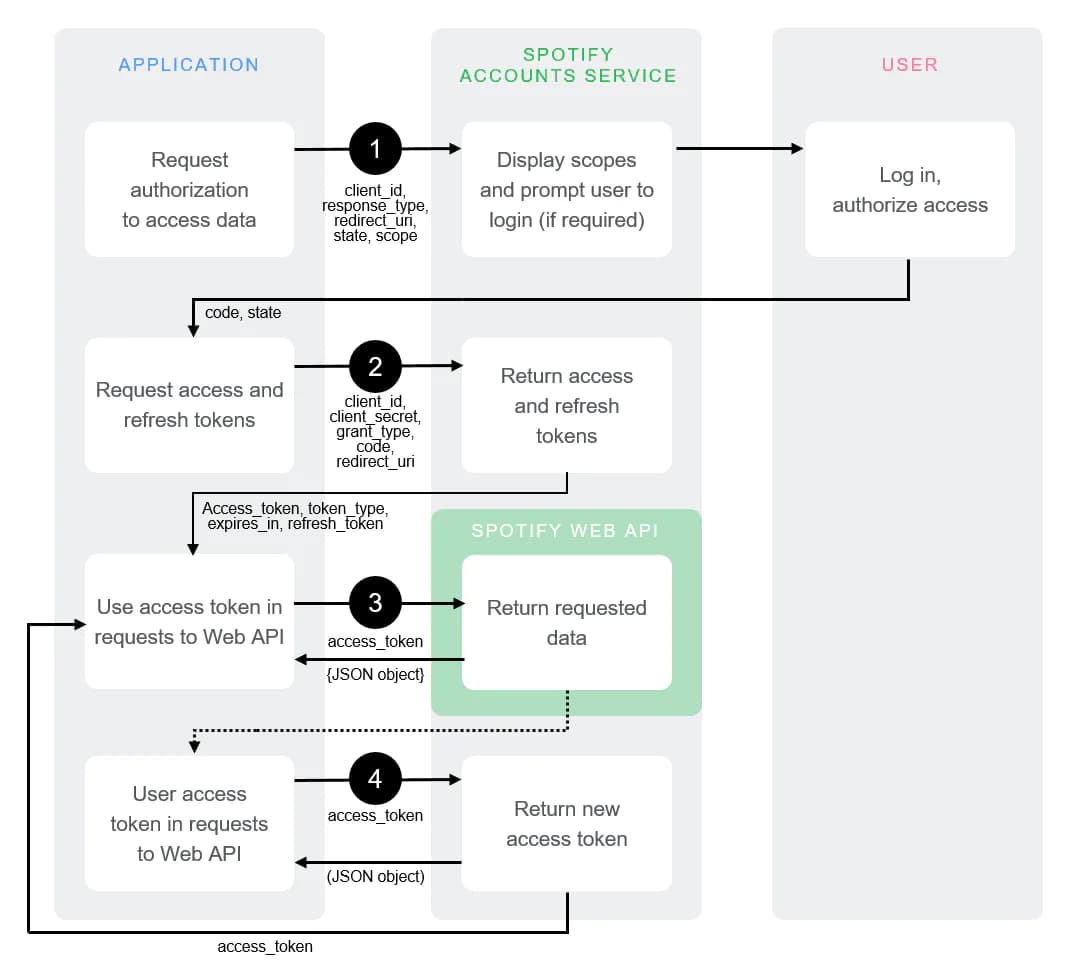
For us to access the Spotify data and features, or to have our app fetch data from Spotify, we need to authorize our application.
We start by preparing the CLIENT_ID. In the link below, replace CLIENT_ID_HERE with the actual CLIENT_ID from your developer
dashboard.
https://accounts.spotify.com/authorize?client_id=CLIENT_ID_HERE&response_type=code&redirect_uri=http
%3A%2F%2Flocalhost:3000&scope=user-read-currently-playing%20user-top-read
Now you need to open the formatted link in a browser (Chrome, Safari etc.). Once the link loads you will get redirected to a uri, copy the website link
Example of the redirect link:
http://localhost:3000/?code=AQBeA9SD7QbA9hUfv_TfmatYxT51CY87msMnOZmMbhf7ZaxfbvG7oKEsATOJBxDyFap0Aq6uftY0v4Hq1QSy3MgQBfAHhmrifty-62rfDRlFnd0AzXRBOMpoOSA6SNw_uTPp7AixAE5zosgiIIf7efhzf1QOJfLh1HUYi248z8jk1x2jjKG2YLvMyJuP0rjB5tP5UHjoFGBvKbULpchkF6yiJHnS
Extract the string after code= as it will be required for the next step.
Next we need to get authorization client that is already encrypted with base64, use this website to encrypt with the format of client_id:client_secret
Write down the encrypted base64 string.
Open up terminal/cmd, and run the command given below. Change CHANGE_BASE64_HERE and CHANGE_CODE_HERE to thier respective values.
curl -H "Authorization: Basic CHANGE_BASE64_HERE"
-d grant_type=authorization_code -d code=CHANGE_CODE_HERE -d redirect_uri=http%3A
%2F%2Flocalhost:3000 https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token
It is important that you format the command as a single line before running it in the terminal.
Example:
curl -H "Authorization: Basic ZWFjY2I5N2Y2ZDBlNDA1ODk3YWRmMWRkODBiOTVjMDE6YTQxOTVjMmQwYTQyNDM2MDllNjk3ZTYwMmU3MGI3NjI=" -d grant_type=authorization_code -d code=AQBeA9SD7QbA9hUfv_TfmatYxT51CY87msMnOZmMbhf7ZaxfbvG7oKEsATOJBxDyFap0Aq6uftY0v4Hq1QSy3MgQBfAHhmrifty-62rfDRlFnd0AzXRBOMpoOSA6SNw_uTPp7AixAE5zosgiIIf7efhzf1QOJfLh1HUYi248z8jk1x2jjKG2YLvMyJuP0rjB5tP5UHjoFGBvKbULpchkF6yiJHnS -d redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost:3000 https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token
This will return a JSON response containing an access_token and a refresh_token. Access tokens are deliberately set to expire after a short time, so we'll need the refresh_token to generate new access_tokens. Make sure you save the value of your refresh_token.
Saving Sensitive Data to ENV file
We don't want our sensitive data like the refresh_token to be exposed when we upload our source code to a repository or a hosting
platform. So we are going to store it in an environment variable. NextJS has it all set up for us using the .env.local file. Make
sure to have a read on it first before you continue.
If you don't use NextJS, you can install the dotenv library on your app.
In your .env.local file, add your client_id, client_secret, and refresh_token.
SPOTIFY_CLIENT_ID=
SPOTIFY_CLIENT_SECRET=
SPOTIFY_REFRESH_TOKEN=
Requesting Access Token
The access token is only valid for a short time so we'll be needing a new token after it expires. For that, we are going to use the refresh token.
Inside your project directory, create a lib/spotify.ts file and paste the code below.
const client_id = process.env.SPOTIFY_CLIENT_ID
const client_secret = process.env.SPOTIFY_CLIENT_SECRET
const refresh_token = process.env.SPOTIFY_REFRESH_TOKEN as string
const basic = btoa(`${client_id}:${client_secret}`)
const NOW_PLAYING_ENDPOINT = `https://api.spotify.com/v1/me/player/currently-playing`
const TOP_TRACKS_ENDPOINT = `https://api.spotify.com/v1/me/top/tracks`
const TOKEN_ENDPOINT = `https://accounts.spotify.com/api/token`
const getAccessToken = async () => {
const response = await fetch(
`${TOKEN_ENDPOINT}?grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=${refresh_token}`,
{
method: 'POST',
headers: {
Authorization: `Basic ${basic}`,
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
}
}
)
return response.json()
}
export const getNowPlaying = async () => {
const { access_token } = await getAccessToken()
return fetch(NOW_PLAYING_ENDPOINT, {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${access_token}`
}
})
}
export const getTopTracks = async () => {
const { access_token } = await getAccessToken()
return fetch(TOP_TRACKS_ENDPOINT, {
headers: {
Authorization: `Bearer ${access_token}`
}
})
}
Create api.ts file in lib directory. The purpose of this file is to handle errors in our api routes.
import type { NextApiResponse } from 'next'
export function isValidHttpMethod(
method: string | undefined,
allowedMethods: string[]
): boolean {
if (!method) {
return false
}
return allowedMethods.indexOf(method) !== -1
}
export const MethodNotAllowed = (res: NextApiResponse) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
return res.status(405).json({ message: 'Method not allowed' })
}
export const MethodNotAllowedEdge = () => {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ message: 'Method not allowed' }), {
status: 405,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
}
export const BadRequest = (res: NextApiResponse, message?: string) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
return res.status(400).json({ message: message || 'Bad request' })
}
export const BadRequestEdge = (message?: string) => {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ message: message || 'Bad request' }), {
status: 400,
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
}
export const Unauthorized = (res: NextApiResponse) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
return res.status(401).json({ message: 'Unauthorized' })
}
export const ServerError = (res: NextApiResponse, error: unknown) => {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
if (error instanceof Error) {
return res.status(500).json({ message: error.message })
} else {
return res.status(500).json({ message: 'Unknown error' })
}
}
It is good practise to set security policy of your app. Hence add the following code to next.config.js file.
/* eslint-disable @typescript-eslint/no-var-requires */
/** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */
const nextConfig = {
reactStrictMode: true,
swcMinify: true,
images: {
domains: ['i.scdn.co']
},
async headers() {
return [
{
source: '/:path*',
headers: securityHeaders
}
]
}
}
const ContentSecurityPolicy = `
default-src 'self';
script-src 'self' 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline' data: https://dhruvg-analytics.vercel.app/umami.js;
child-src 'self';
style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline';
img-src * blob: data:;
media-src 'none';
connect-src *;
font-src 'self';
`
const securityHeaders = [
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP
{
key: 'Content-Security-Policy',
value: ContentSecurityPolicy.replace(/\n/g, '')
},
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Referrer-Policy
{
key: 'Referrer-Policy',
value: 'origin-when-cross-origin'
},
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Frame-Options
{
key: 'X-Frame-Options',
value: 'DENY'
},
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Content-Type-Options
{
key: 'X-Content-Type-Options',
value: 'nosniff'
},
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-DNS-Prefetch-Control
{
key: 'X-DNS-Prefetch-Control',
value: 'on'
},
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Strict-Transport-Security
{
key: 'Strict-Transport-Security',
value: 'max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload'
},
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Feature-Policy
{
key: 'Permissions-Policy',
value: 'camera=(), microphone=(), geolocation=()'
}
]
module.exports = nextConfig
Notice that I have added
i.scdn.coin the domains array of images object. This is because you need to whitelist external image URL's in Next
Top Tracks Data from Spotify
Create a top-tracks.ts file in pages/api directory of your next app and paste the following code
import type { NextApiRequest } from 'next'
import { getTopTracks } from '@/lib/spotify'
import { isValidHttpMethod, MethodNotAllowedEdge } from '@/lib/api'
export const config = {
runtime: 'experimental-edge'
}
type ResponseTrackType = {
artists: {
name: string
}[]
name: string
external_urls: {
spotify: string
}
album: {
images: {
url: string
}[]
}
}
export default async function handler(req: NextApiRequest) {
if (!isValidHttpMethod(req.method, ['GET'])) {
return MethodNotAllowedEdge()
}
const response = await getTopTracks()
const { items } = await response.json()
const tracks = items.slice(0, 10).map((track: ResponseTrackType) => ({
artist: track.artists.map(_artist => _artist.name).join(', '),
songUrl: track.external_urls.spotify,
cover: track.album.images[1]?.url,
title: track.name
}))
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ tracks }), {
status: 200,
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json',
'cache-control': 'public, s-maxage=86400, stale-while-revalidate=43200'
}
})
}
If everything worked correctly, you should see some data like this https://dhruvgursahani.vercel.app/api/top-tracks
Now Playing Data from Spotify
Inside you pages/api directory create a now-playing.ts file and paste the code given below.
import { type NextRequest } from 'next/server'
import { getNowPlaying } from '@/lib/spotify'
import { isValidHttpMethod, MethodNotAllowedEdge } from '@/lib/api'
export const config = {
runtime: 'experimental-edge'
}
export default async function handler(req: NextRequest) {
if (!isValidHttpMethod(req.method, ['GET'])) {
return MethodNotAllowedEdge()
}
const response = await getNowPlaying()
if (response.status === 204 || response.status > 400) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ isPlaying: false }), {
status: 200,
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
}
})
}
const song = await response.json()
if (song.item === null) {
return new Response(JSON.stringify({ isPlaying: false }), {
status: 200,
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json'
}
})
}
const isPlaying = song.is_playing
const title = song.item.name
const artist = song.item.artists
.map((_artist: { name: string }) => _artist.name)
.join(', ')
const album = song.item.album.name
const albumImageUrl = song.item.album.images[0].url
const songUrl = song.item.external_urls.spotify
return new Response(
JSON.stringify({
album,
albumImageUrl,
artist,
isPlaying,
songUrl,
title
}),
{
status: 200,
headers: {
'content-type': 'application/json',
'cache-control': 'public, s-maxage=60, stale-while-revalidate=30'
}
}
)
}
On browsing this endpoint you would get a response in the following format.
{
"album": "Beat the Odds",
"albumImageUrl": "https://i.scdn.co/image/ab67616d0000b2732ac708dff220b6644e9c67e5",
"artist": "Lil Tjay",
"isPlaying": true,
"songUrl": "https://open.spotify.com/track/2BJWxD8xKrDv8vneTvTIm9",
"title": "Beat the Odds"
}
Wrap up 🔚
Thanks for reading!
Comments